Outsourcing
Definition and Overview of Outsourcing
Outsourcing is the transfer to an external service provider the operation and day-to-day management of a business process, with the aim to achieve increased productivity, cost effectiveness and system efficiency.
Outsourcing can be defined as a process in which a company enters into a contract with another company to operate and manage one or more of its business processes.
It involves the general business practice through which firms cut costs by transferring a portion or an entire organizational function to an external agency located either domestically or abroad rather than performing it internally.
- Outsourcer refers to a company that contracts with another company to provide services that might otherwise be performed by its in-house employees.
- The service provider or external company is called vendor.
Vendors are experts in the jobs and in addition they have domain knowledge of the customer’s industry. They are either standalone outfits, i.e., experts in one particular activity or integrators having expertise in multiple functional areas. The integrators have the capabilities to integrate them as per the customer’s needs.
The concept of outsourcing started with Ross Perot when he founded Electronic Data Systems in 1962. EDS would tell a prospective client,
You are familiar with designing, manufacturing and selling furniture, but we’re familiar with managing information technology. We can sell you the information technology you need, and you pay us monthly for the service with a minimum commitment of two to ten years. — Ross Perot, EDS
Thus, outsourcing involves the delegation of tasks or jobs from internal production to an external entity (such as a subcontractor). This means buying goods or services instead of producing or providing them in-house. Thus, a firm’s decision to outsource falls within the class of ‘make’ or ‘buy’ decisions (Walker and Weber, 1984).
Outsourcing is an effective cost-saving strategy when applied properly. It is sometimes more economical to purchase goods or services from firms with comparative advantages than it is to produce these goods or services internally. In this case, a firm may decide to tactically outsource its bookkeeping function to an external accounting firm, as it may be more cost effective to do so than managing it internally with in-house accountants.
General Electric, for example, has outsourced about 900 different business processes to India and as a result saves nearly $350 million annually. — The Boston Consulting Group and University of Pennsylvania, The Wharton School, 2007
The sole purpose of outsourcing is to save money, improve quality, or free company resources for other activities. Outsourcing was first done in the data-processing industry and has spread to other areas including telemarketing and call centres.
Many large companies now outsource jobs such as call centre services, e-mail services, and payroll. These jobs are handled by separate companies specializing in each service.
Many of the companies that provide outsourcing services are able to do the same work for considerably less money, as they have the expertise to complete the job in the shortest possible time.
Although outsourcing is an old concept in the manufacturing industry, where most large manufacturers of mass-produced goods have traditionally used specialized vendors to supply sub-assemblies. Today, outsourcing continues to move into more strategic areas of the business.
The firms are realizing that their best partner is the one that offers them the greatest value, not necessarily the lowest cost. Most business firms which go for outsourcing follow the following decision model, shown in Figure I.
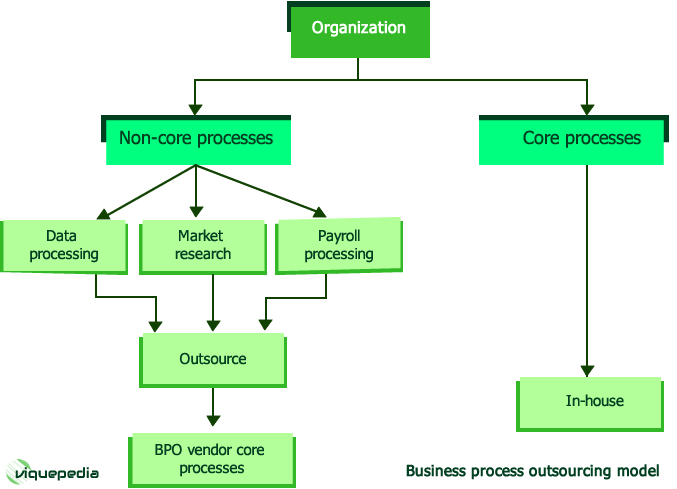
|
In the high-tech industry, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) like Cisco, IBM, Nortel, Palm, and Compaq have outsourced manufacturing to specialists like Solectron and Celestica. These contract manufacturers have expanded their services to include shipping, repairs, and even product design. Thus by offering design services, the contract manufacturers help OEMs craft products in a more standardized way to cuts costs and reduce the risk of component shortages, which can hurt a Cisco or a Compaq badly.
Advantages of Outsourcing
There are some definite advantages to outsourcing. Outsourcing creates shareholder value by reducing costs and commitments to fixed and working capital. Following are often cited advantages of outsourcing.
- One of the major advantages of outsourcing is flexibility. It can be a lot easier to cut back on a vendor than an employee.
- Contract work is often cheaper—especially if opted for off-shore development. Here, people are hired only for specific tasks.
- Outsourcing helps a firm focus on its core business, helping to create a competitive advantage within its industry.
- Another advantage that the firms have is that they can attain expertise in every particular area.
- The most positive thing about outsourcing is its ability to save a firm’s money. This will depend on the size of the company and what specific tasks are to be outsourced. For example, a company outsources the IT services (help desk, computer support and maintenance) and pays significantly less than they pay a full-time IT person to give the same level of support.
- Another advantage outsourcing gives firms is a chance to get the best job possible from the vendors it hires. However, if the work is done in-house, there may be company ties which are hard to break.
There are some disadvantages of outsourcing as well, particularly in marketing outsourcing.
- One is that outsourcing often eliminates direct communication between a firm and its clients. This prevents the firm form building strong relationships with their customers, and often leads to dissatisfaction on one or both sides.
- There is also the danger of not being able control some aspects of the business, as outsourcing may lead to delayed communications and project implementation.
- The sensitive information is more vulnerable, and the firm may become very dependent upon its outsource providers, which could led to problems in the event of the outsourcing service provider backing out of the contract suddenly.
Thus, while outsourcing may prove beneficial on many counts, it also has many drawbacks. It is important that each individual company accurately assesses its need to determine if outsourcing is a viable option.
Outsourcing Guidelines
The goal of outsourcing is better quality at lower costs, but too often the outsourcing results are disappointing-to-dismal; the reason is that many buyers lack a clear outsourcing methodology. Using the outsourcing concepts, managers responsible for outsourcing should follow the following steps:
- Determine core competencies that should be kept in-house rather than outsourced
- Align outsourcing with overall corporate strategy
- Use outsourcing to support transformation strategies such as restructuring and TQM
- Evaluate, compare, and select vendors
- Negotiate win-win contracts, monitor how vendors perform, and evaluate financial savings
- Handle competition from vendors’ as well as contractors’ end.
The costs involved in managing the outsourcing process can be a cause for worry, but it need not be so. Firms need to make sure that there is clarity in planning out management strategies and adapting them to outsourcing.
Irrespective of the size of business, for getting benefits out of outsourcing, a proper management framework to organize the process is integral. Better outsourcing management helps in optimizing resources for maximum performance.
There are certain areas of outsourcing business that need constant attention. Concentrating on these areas will greatly increase control over the direction of the outsourced project.
Cost
The main attraction of outsourcing is its cost reduction. To achieve this, firms must analyze the scope and price right at the beginning of the project and arrive at a reasonable consensus on cost.
Communication
It is essential to establish proper communication channels that facilitate open communication. The main advantage of maintaining good communication with the BPO partner is transparency in all activities. To ensure better communication the following should be in place:
- Establish good communication systems
- Regularly contact the outsourcing partner
- Give clear instructions and feedback
- Give clear instructions and feedback
- Clarify all possible doubts that can arise.
Performance
It is necessary to strike a balance between the actual performance levels and the ideal performance standards of the outsourcing project. The core issue in performance management is the time factor. It is important to make sure that the project does not lag too much. To ensure this, targets have to be specified, and review and analysis has to be done on a regular basis.
Risk Management
Risk factors are the biggest sources of concern in outsourcing. A complete assessment of possible risks will give an upper hand in being aware of various risks and ensuring that they are managed well.
Crisis Management
Firms need to ensure that the management is financially and professionally equipped to deal with contingencies. With a good outsourcing partner, crisis management will not be a difficult issue as contingencies are supported with back-up plans.
Knowledge Transfer
Knowledge transfer has a direct influence on productivity. Hence, while transferring knowledge about the proposed project, there is need to make sure that complete information and knowledge is transferred to one’s outsourcing partner.
Relationship
In the outsourcing business, both the parties enter into a long-term relationship for mutual benefit. As far as possible, business should be done with an ethical and credible partner. This will add to the profitability of business as the cost of maintaining the relationship will be reduced. In addition to evaluate the outsourcing partner, the outsourcing firm needs to know how to equip in-house capabilities to match with requirement. For this, they need to
- Evaluate in-house capability
- Distribute the workload between in-house and outsourcing processes
- Entrust a responsible person or team to monitor the outsourcing process
- Train employees on how to manage and organize an outsourcing business
Ultimately, the aim is to succeed in its outsourcing venture and that too with considerable profit margin. There is a need to establish the best possible management systems for going ahead with outsourcing of business processes.
related literatures:
- M.S. Rangaraju, S. Hanuman Kennedy, Management Challenges and Opportunities in the next decade, (p. 60) Introduction to BPOs, edited by Nagaraj Shenoy.
- Rick L. Click, Thomas N. Duening, Business Process Outsourcing: The Competitive Advantage, (p.3-9) What Is So Revolutionary about BPO?
- Vinod V. Sople. Business Process Outsourcing: A Supply Chain of Expertises, (p. 20) Need for Outsourcing.

